Go green with AT #3: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
What is Artificial Intelligence?
The European project Advanced Technology for Industry (ATI) – who has derived the 16 Advanced Technologies this article series – defines Artificial Intelligence as follows:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a term used to describe machines performing human-like cognitive functions (e.g. learning, understanding, reasoning or interacting). It comprises different forms of cognition and meaning understanding (e.g. Speech recognition, natural Language processing) and human interaction (e.g. signal sensing, smart control, simulators). In terms of its technology base AI is a very heterogeneous field. While some aspects like sensors, chips, robots as well as certain applications like autonomous driving, logistics or medical instruments refer to hardware components, a relevant part of AI is rooted in algorithms and software.

For the less technical reader, the online start-up an tech community Builitin has made an easy article about what AI is, you can read it here. Here, Schroer (2023) explain AI very simple by,
Broadly speaking, artificially intelligent systems can perform tasks commonly associated with human cognitive functions — such as interpreting speech, playing games and identifying patterns. They typically learn how to do so by processing massive amounts of data, looking for patterns to model in their own decision-making. In many cases, humans will supervise an AI’s learning process, reinforcing good decisions and discouraging bad ones. But some AI systems are designed to learn without supervision — for instance, by playing a video game over and over until they eventually figure out the rules and how to win.
Furthermore, some practical every-day examples of AI is given:
- Siri, Alexa and other smart assistants
- Self-driving cars
- Conversational bots
- Email spam filters
- Netflix’s recommendations
In the below video, you can view a 12 min simple outline of what AI is and its historical development.
How can AI be used in manufacturing?
The AI Innovation Center in Einhoven, Netherlands, are actively working with AI and its use and impact on manufacturing sector. Read about their initiatives and informative material on their webpage here. In short, they outline some examples of how AI can be useful in manufacturing through its extensive data collection abilities:
- Track core KPIs and metrics like OEE, production rate, or scrap rate (smart factory)
- Forecast accurate delivery dates and avoid missing deadlines (supply chain)
- Spot and fix equipment inefficiencies as and when they develop (connected worker)
- Spot attacks across cloud services and IoT devices and interrupt them in seconds (cybersecurity)
- Reduce waste and energy use in production facilities (sustainability)
Examples of how I can contribute to greener manufacturing
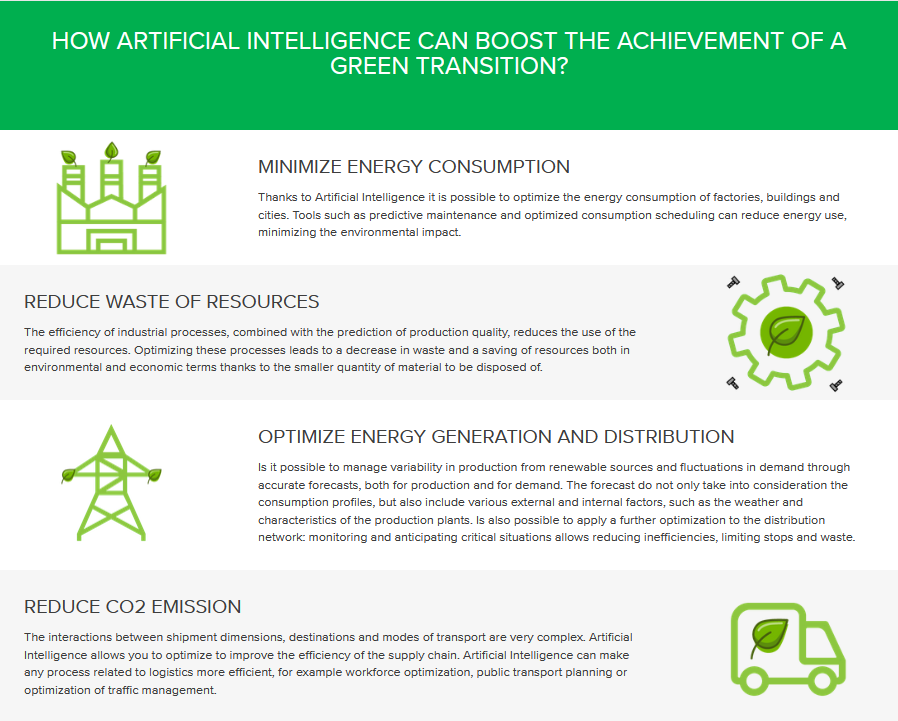
It is well known that implementing new AI systems in companies is often realted to high start up costs. Nevertheless, there are vast benefits to be made, not only for business and profit, but also for green and social sustainability. Reply.com, a innovation and technology consultancy company has summarized 4 aspects of how AI can contribute to the green transition, all highly relevant for the manufacturing sector.
The AI innovation center in Eindhoven has also specified some areas of where AI can be useful for sustainability (read full article here) :
- In agriculture, AI can improve crop yields by strengthening monitoring ands managing systems, as well as water and fertilizer management.
- In energy, AI can improve mainteinance systems and therefore reduce energy consumption. Furthermore, by more accurately predicting weather patterns, AI can optimize efficiency, cutting costs and carbon pollution.
- In transportation, AI can help reduce traffic congestion, improve supply chain logistics, and enable autonomous driving capabilities. AI can also forecast demand, with can help reduce needed transportation.
- In water resource management, AI can help reduce waste and costs for improved environmental impact.
- In manufacturing, AI can help reduce waste and energy use in production, as well as contribute to precise and efficient systems.
- In facilities management, AI can improve heating and cooling systems, and optimize energy use by tracking the number of people in a room.
- In materials science, AI can help researchers find new (CO2 absorbent) materials for solar panels, and for turning heat back into electricity.

In the greenSME Learning Session on Predictive Maintenance, we dig deeper into how AI and big data can improve sustainability in manufacturing through predictive maintenance systems. See it here in the knowledge HUB.
References
Advanced Technology for Industry (2021): https://ati.ec.europa.eu/technologies/artificial-intelligence)
AI Innovation Center BRAINPORT in Einhoven, Netherlands: https://aiinnovationcenter.nl/manufacturing-carbon-footprint/ ; https://aiinnovationcenter.nl/ai-manufacturing/
Schrorer (2023), on BuiltIn.com: https://builtin.com/artificial-intelligence