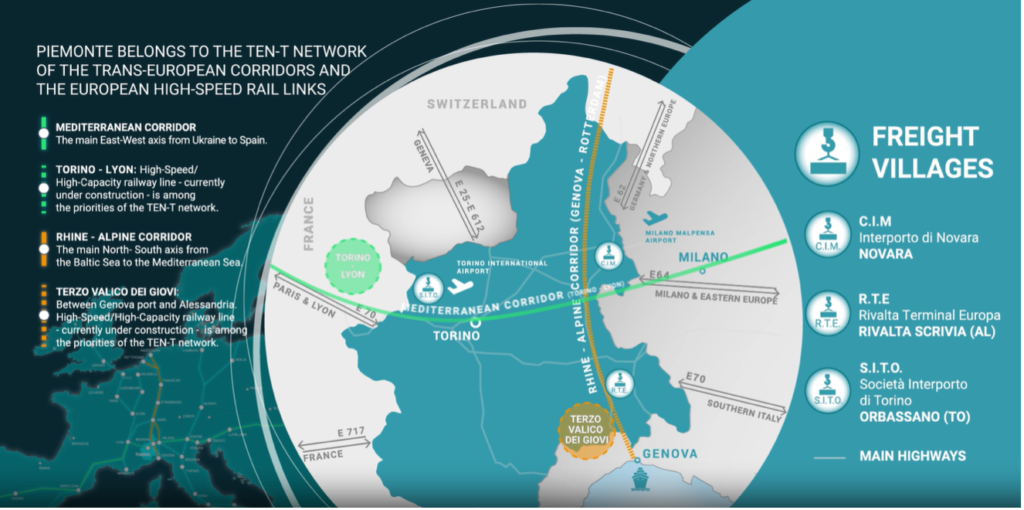
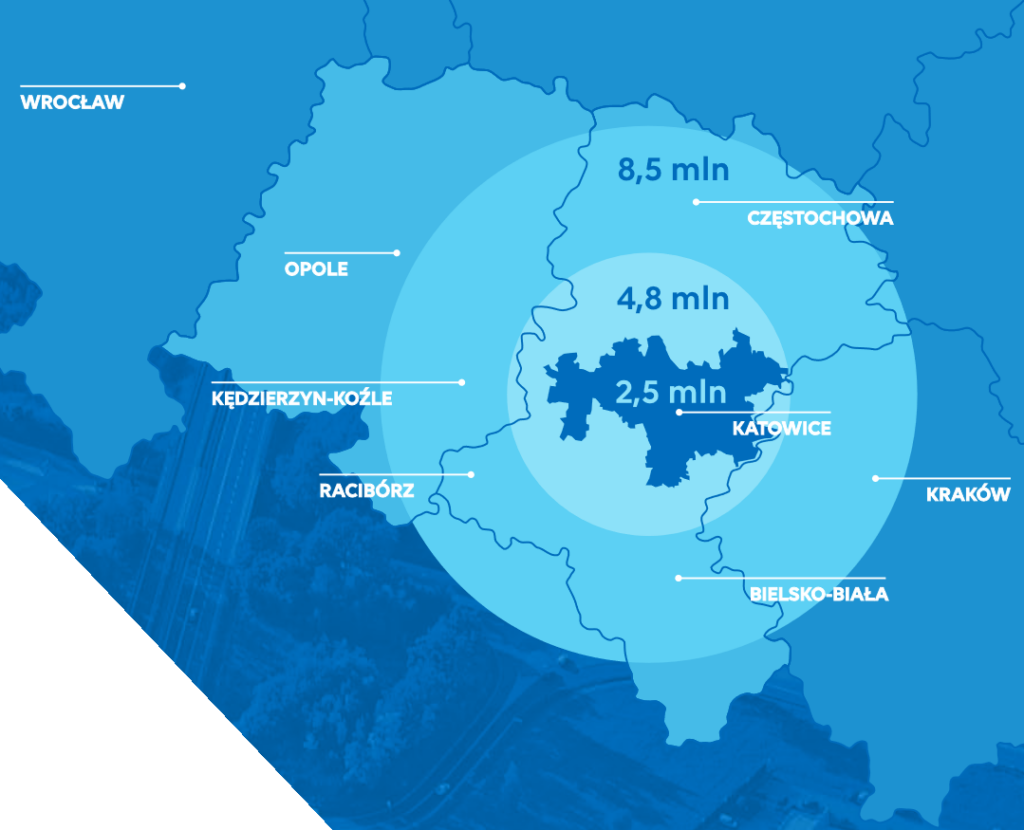
Initial European Sustainable Manufacturing Ecosystem Roadmap
This report describes the initial roadmap for a European Sustainable Manufacturing Ecosystem (EUSME). It develops a strategy and a pathway towards a well-functioning, self-sustaining Europe-wide ecosystem that supports manufacturing SMEs in becoming (more) sustainable in the time until 2035.
It addresses all stakeholders of the EUSME and provides a common vision of how the EUSME should be, and what it should do and have. It identifies gaps between this vision and the current status of the EUSME and suggests a way forward to close these gaps.
The EUSME is understood as a Europe-wide ecosystem that leads to sustainably acting and producing manufacturing SMEs in the European manufacturing industry. Thus, it also relies on those stakeholders that provide second-level support for regional manufacturing clusters and includes for example meta-clusters and sector associations. Besides the European level, it also encompasses the relevant stakeholders on the local or regional and national levels. On each level there are stakeholders involved, who represent the quadruple helix of policy, research and education, economy and civil society. The EUSME is understood as a mission-oriented innovation ecosystem working towards sustainability among manufacturing SMEs.
The understanding of sustainability is based on the three pillars of sustainability the European Green Deal describes. There are the environmental, economic and social sustainability pillars. As this roadmap is dedicated to the manufacturing sector, the goals of the EUSME focus on the implementation of innovations that foster sustainability of manufacturing SMEs in a quick, effective and efficient way.
The situation of SMEs and in particular manufacturing SMEs is, that they often adopt a “green attitude” (Sohns et al 2023), but rarely succeed in implementing more environmental sustainability into their business models. There are specific reasons, that studies have worked out: a lack of time and resources, a strong focus on day-to-day business, high pressure from customers, the difficulty of SMEs to know which technologies are the best fit, less access to finance than larger companies, perceived overburden with compliance issues and the speed of innovation (Martins et al., 2022).
Overarching external trends also challenge manufacturing SMEs. Those are the digital transformation and its speed, changes in legislation that require fast and extensive changes in compliance reporting and gathering data within the organisation, higher costs of materials and energy, inflation and higher interest rates at the same time, rising wage costs and a decline in available workers with the right skills as well as other employee-related problems caused by the demographic change towards ageing societies in Europe as well as insecurities caused by disrupted supply chains that started in the Covid-19 pandemic.
The vision of the EUSME 2035 is to overcome these challenges of manufacturing SMEs by working together. The overarching goals of the EUSME can be summarised as follows.
- The twin transition of manufacturing SMEs will be accelerated by the provision of intuitive methods and tools of adaptation for the SMEs.
- SMEs will be enabled to implement advanced manufacturing technologies in their existing business that increase sustainability. They will receive support with the necessary tools and expertise to ensure their competitiveness through a sustainable production process.
- The EUSME as an ecosystem with the mission of fostering sustainability of manufacturing SMEs, needs to find a common vision, common goals and a common way of communicating these in order to act together towards the common goal. In order to find a common message and strategy, a group with a holistic view can lead this collaborative process.
- The stakeholders will have a common understanding of shared responsibilities and the impact they should have in supporting manufacturing SMEs.
- The European Sustainable Manufacturing Ecosystem is built on collaboration. The quadruple helix of stakeholder groups from the societal fields of public policy, economy, research & education and civil society work together looking for synergies to ensure innovation for a sustainable manufacturing industry. The whole value chain is engaged in the ecosystem, even the smallest companies.
- As it is difficult to engage all sectors in all countries, networks with different layers of organisation are necessary: regional and local networks (including cluster organisations), national networks (e.g. national sector or business associations, policy makers etc.) and Europe-wide networks (mainly the meta-clusters and possible policy makers) as described above.
- The ecosystem supports the overall goal of positioning Europe against other regions of the world, e.g. North America, China and Russia in order to stay competitive and find solutions of sustainability for manufacturing SMEs despite current trends of SMEs losing ground.
- The EUSME aims to develop activities that foster collaboration, the exchange of experiences and learning. For that, within the ecosystem, it will be made effective use of previous experiences (such as success cases).
The road mapping process of the greenSME project will continue to develop a more comprehensive and detailed roadmap towards a successful EUSME in 2035. The final roadmap will be developed in another dedicated deliverable of the greenSME project.